Share This Article
Marketers, sales managers, and marketing agencies constantly face the challenge of finding fresh, high-quality leads. Traditional methods can be time-consuming, expensive, and often yield outdated information. Generating targeted local business contacts efficiently is crucial for outreach campaigns, market research, and competitive analysis. Imagine needing a list of all cafes in Chicago or plumbers in Austin – manually compiling this data from Google Maps is a daunting task prone to errors and inefficiency. This is where specialized tools come into play, transforming a laborious process into a streamlined operation. One powerful solution designed specifically for this purpose is the Google Maps Scraper, which allows for the seamless export of local business contacts directly from Google Maps.
What Is Google Maps Scraper?
The Google Maps Scraper is a specialized software tool designed to automate the extraction of business information from Google Maps. At its core, it’s a data harvesting tool that targets Google Maps listings, pulling details like business names, addresses, phone numbers, websites, ratings, review counts, and sometimes even email addresses and social media profiles (where available). Instead of manually searching, copying, and pasting data for each business, users can define their search criteria (e.g., business type, location), and the scraper systematically gathers this information, organizing it into a structured file format like CSV or Excel. This makes it an invaluable asset for anyone needing comprehensive local business data for marketing, sales, or research purposes.
Why It Matters for Marketers, Agencies, and Sales
In today’s competitive landscape, access to accurate and targeted data is paramount. For marketers, marketing agencies, and sales managers, the ability to quickly identify and connect with potential local clients or understand the local market dynamics is crucial for success. Here’s why a tool like Google Maps Scraper is so important:
- Lead Generation Engine: It provides a direct pipeline to potential B2B clients in specific geographical areas and industries. Sales teams can build highly targeted prospect lists for cold outreach, significantly increasing efficiency compared to manual prospecting.
- Market Research: Agencies and marketers can analyze the density of specific business types in a region, understand competitor landscapes, identify underserved areas, or gauge market saturation. This data informs strategic decisions and campaign planning.
- Local SEO Analysis: While focused on contact extraction, the data (like review counts and ratings) can offer insights into the online reputation and visibility of local businesses, complementing local SEO efforts. Understanding the competitive landscape helps agencies tailor their strategies.
- Database Enrichment: Existing customer or prospect databases can be updated or enriched with current contact information, location details, and operational hours sourced directly from Google Maps, ensuring data accuracy.
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Manual data collection is incredibly time-consuming and expensive when factoring in labor costs. Automating this process frees up valuable time for teams to focus on strategy, outreach, and closing deals rather than data entry.
Furthermore, leveraging precise local data enhances personalization efforts. Sales pitches and marketing campaigns can be tailored to the specific location and context of the prospect, increasing relevance and response rates. While tools focused on website analysis address different needs – sparking questions like ‘What is SiteGuru?’ for technical SEO audits – the Google Maps Scraper specifically tackles the challenge of local business lead generation at scale.
How Google Maps Scraper Works
Understanding the mechanism behind the Google Maps Scraper clarifies its power and efficiency. While specifics can vary slightly between different tools implementing this concept, the general process involves several key steps:
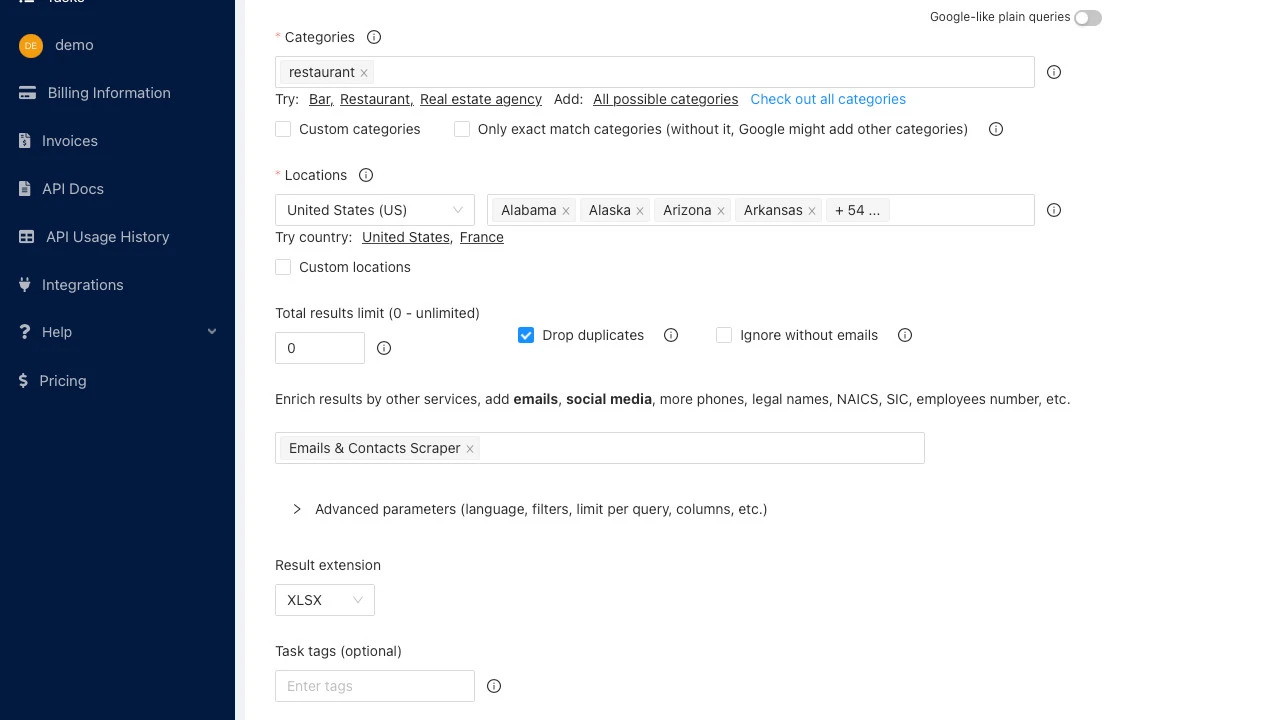
- Defining Search Parameters: The user starts by inputting the desired search criteria. This typically includes the type of business (e.g., “restaurants,” “digital marketing agencies,” “dentists”) and the geographical location (e.g., “New York City,” “California,” “ZIP code 90210”). Some tools might allow for more advanced filtering, such as specifying businesses with websites or those within a certain rating range.
- Automated Searching: The software then interacts with Google Maps, simulating user searches based on the parameters provided. It systematically queries Google Maps for businesses matching the criteria within the specified location(s).
- Data Extraction: As Google Maps returns search results (listings), the scraper identifies and extracts the relevant data points associated with each listing. This includes information publicly available on the map listing, such as:
- Business Name
- Full Address (Street, City, State, ZIP Code)
- Phone Number
- Website URL
- Google Maps Rating (e.g., 4.5 stars)
- Number of Reviews
- Business Category (e.g., “Italian Restaurant”)
- Operating Hours (sometimes)
- Plus Code (Geographical coordinate)
- Potentially emails and social links if listed publicly or inferred
- Data Compilation and Deduplication: The extracted data is collected and organized. Good scrapers often include mechanisms to remove duplicate entries that might appear across slightly different searches or locations, ensuring a cleaner final list.
- Exporting Data: Finally, the compiled data is made available for download in a structured format, commonly CSV (Comma Separated Values) or Excel (XLSX). This allows users to easily import the data into CRMs, spreadsheets, email marketing platforms, or other analytical tools.
The process is designed to be much faster and more comprehensive than manual searching, capable of gathering data on hundreds or even thousands of businesses in a fraction of the time.
Key Features and Benefits
The Google Maps Scraper offers a suite of features designed to maximize efficiency and data quality for its users. Here are some of the core functionalities and the benefits they provide:
- Feature: Targeted Data Extraction
- Benefit: Allows users to specify business categories and locations, ensuring the extracted data is highly relevant to their campaign goals. This precision saves time filtering irrelevant contacts later.
- Feature: Comprehensive Data Points
- Benefit: Goes beyond just name and address to capture phone numbers, websites, ratings, review counts, and potentially emails/social links. This richer dataset enables more informed outreach and analysis.
- Feature: Bulk Exporting Capabilities
- Benefit: Exports gathered data into universally compatible formats like CSV or Excel. This makes integration with existing CRM systems, sales tools, and marketing platforms seamless.
- Feature: Automation and Speed
- Benefit: Drastically reduces the time and manual effort required for lead generation and market research. What could take days of manual work can often be accomplished in minutes or hours.
- Feature: Scalability
- Benefit: Capable of handling large-scale data extraction tasks, whether targeting a single neighborhood or multiple cities/states. This supports growth and expansion efforts.
- Feature: Data Accuracy (Relative to Source)
- Benefit: Pulls data directly from Google Maps listings, which businesses often keep updated. While not infallible, it’s generally more current than static, pre-compiled databases.
- Feature: Potential for Email and Social Media Scraping
- Benefit: Some scrapers attempt to find associated email addresses (often from the business website linked on Maps) and social media profiles, adding valuable channels for outreach. However, it’s crucial to ensure compliance with outreach regulations. Ensuring the quality of these emails is vital; consider resources on how to Boost Email Deliverability with Reoon Verifier.
These features collectively empower marketers, agencies, and sales teams to build robust lead lists, conduct thorough market research, and ultimately drive more targeted and effective campaigns.

Pros and Cons
Like any tool, the Google Maps Scraper comes with its own set of advantages and potential drawbacks. Understanding these helps set realistic expectations:
Pros:
- Efficiency Boost: Massively accelerates the process of gathering local business data compared to manual methods.
- Targeted Lead Generation: Enables the creation of highly specific prospect lists based on industry and location.
- Rich Data Sets: Often extracts more than just basic contact info, including websites, ratings, and review volume.
- Cost-Effective (Potentially): Compared to purchasing expensive pre-compiled lists (which may be outdated) or paying for hours of manual labor, scraping can offer better ROI, especially with advantageous deals. Exploring options like lifetime software deals can maximize this benefit. Learn more in The Ultimate Guide to Lifetime SaaS Deals.
- Supports Market Analysis: Provides valuable data for understanding local market structures and competitor presence.
Cons:
- Data Accuracy Limitations: The accuracy is dependent on the information businesses provide on Google Maps. Outdated listings will yield outdated data.
- Email Address Availability: Finding direct email addresses can be hit-or-miss, as many businesses don’t list them publicly on Maps. Scrapers might try to find them on linked websites, but success isn’t guaranteed.
- Terms of Service Considerations: Users should be aware of Google’s Terms of Service regarding automated data collection. Using scrapers responsibly is important.
- Potential for Technical Issues: Like any software, scrapers can encounter temporary issues due to changes in Google Maps’ structure or anti-bot measures.
- Requires Proper Usage Strategy: Simply having the data isn’t enough. Effective outreach strategies and compliance with communication regulations (like CAN-SPAM or GDPR) are essential.
Weighing these pros and cons helps determine if a Google Maps Scraper aligns with your specific needs and operational practices.
Best Use Cases
The versatility of the Google Maps Scraper makes it suitable for various applications across different roles:
- Sales Managers: Building targeted prospect lists for sales development representatives (SDRs) based on territory and ideal customer profile (ICP). Identifying new businesses entering a specific market.
- Marketing Agencies: Generating leads for their own services (e.g., finding local businesses that might need web design, SEO, or social media marketing). Conducting competitor analysis for clients by mapping out similar businesses in their service area. Identifying businesses with poor reviews as potential clients for reputation management services.
- Local Marketers: Creating lists for direct mail campaigns, local event invitations, or partnership outreach within a specific community or neighborhood.
- Market Researchers: Gathering data for studies on business density, industry distribution across geographic areas, or average business ratings within a sector.
- Franchise Development: Identifying potential locations for expansion by analyzing the presence and performance of competitors or complementary businesses.
- Event Planners: Finding potential local sponsors, vendors, or attendees for conferences and events.
- Real Estate Developers: Analyzing the commercial landscape of an area to understand existing services and potential gaps.
Essentially, any role or business that relies on connecting with local businesses or understanding the local commercial environment can benefit significantly from the data provided by a Google Maps Scraper.

How to Get Started
Getting started with a tool like the Google Maps Scraper is typically straightforward. Here’s a general guide:
- Access the Tool: Visit the provider’s website or platform where the scraper is offered. This might involve signing up for an account or purchasing access.
- Define Your Task: Navigate to the scraping section or task creation area. You’ll need to input your specific requirements:
- Keywords/Categories: Enter the types of businesses you’re looking for (e.g., “Coffee Shops,” “Hardware Stores”).
- Location(s): Specify the city, state, ZIP code, or broader region you want to target. Some tools allow multiple locations per task.
- Advanced Filters (Optional): Configure any additional filters if available, such as minimum rating, presence of a website, etc.
- Initiate the Scraping Process: Launch the task. The software will begin querying Google Maps based on your inputs. The time required will depend on the number of potential results and the tool’s speed.
- Monitor Progress (Optional): Many tools provide a dashboard where you can see the status of your scraping task and the number of leads found so far.
- Download Your Data: Once the task is complete, you’ll typically receive a notification. Navigate to the results or downloads section and export the data, usually as a CSV or Excel file.
- Review and Utilize: Open the downloaded file. Clean or format the data as needed (though good scrapers minimize this). Import the list into your CRM, email marketing tool, or sales engagement platform to begin your outreach or analysis. Remember to use data responsibly and ethically. For instance, if collecting social media handles, consider tools and strategies to Streamline Social Media & Boost ROI with Sociamonials.
Most providers offer documentation or tutorials to guide users through these steps specific to their interface.
Conclusion: Unlock Local Leads with Efficiency
For marketers, sales teams, and agencies striving to connect with local businesses, the manual process of data collection from Google Maps is a significant bottleneck. The Google Maps Scraper emerges as a powerful, efficient solution to this challenge. By automating the extraction of vital business information – names, addresses, phone numbers, websites, ratings, and more – it transforms lead generation and market research.
This tool empowers users to build highly targeted lists, gain valuable market insights, enrich existing databases, and ultimately save countless hours of manual labor. While awareness of data accuracy limitations and responsible usage is important, the benefits in terms of efficiency, scalability, and access to rich local data are undeniable.
If you’re looking to supercharge your local outreach, understand your market better, or simply stop spending valuable time on manual data entry, exploring a Google Maps Scraper is a strategic move. It provides the data foundation needed to drive more effective marketing and sales campaigns in any local market.
Related Reading
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Is scraping Google Maps legal?
Automated data scraping exists in a legal gray area and often depends on the methods used and how the data is utilized. Google’s Terms of Service generally discourage automated scraping. It’s crucial to use scraping tools responsibly, avoid overloading servers, and respect privacy regulations (like GDPR) and communication laws (like CAN-SPAM) when using the extracted data for outreach.
How accurate is the data from a Google Maps Scraper?
The data accuracy is directly tied to the accuracy of the information listed on Google Maps itself. Businesses are generally incentivized to keep their listings current, but outdated information can exist. The scraper pulls what is publicly available; it doesn’t independently verify the data beyond what’s on the listing.
Can I get email addresses for all businesses?
No, not always. Email addresses are often not listed directly on Google Maps business profiles. While some advanced scrapers attempt to find emails by visiting the website linked in the Maps listing, success rates vary significantly. Don’t expect a 100% email find rate for all extracted contacts.
What formats can I export the data in?
Most Google Maps Scrapers, including the Google Maps Scraper tool mentioned, typically allow exporting data into common structured formats like CSV (Comma Separated Values) and Excel (XLSX). This ensures easy compatibility with spreadsheets, CRMs, and other business software.
Is there a limit to how much data I can scrape?
Limits usually depend on the specific tool provider and the plan or purchase tier you have. Some might limit the number of records per task, the number of tasks per day/month, or operate on a credit system where each extracted record consumes credits. Review the provider’s terms for specific limitations.

 Software
Software
